Most impotently wind load on overhangs is very critical as both of the surfaces ie. Note 8 of Figure 286-1 of ASCE7-10 states emphasis mine Where zone E or G falls on a roof overhang on the windward side of the building use E OH and G OH for the pressure on the horizontal projection of the overhang.

Wind Load Provisions In The Ubc Civil Engineering
Wind Loads on NonStandard Building Configurations.
Building overhang wind design asce. Because the building has a monoslope roof the roof surface for wind directed parallel to the slope may be windward or leeward. Kostenlose Lieferung für viele Artikel. Finden Sie Top-Angebote für Design of Buildings for Wind.
The analytical procedure is used to determine design wind pressures for the main wind force-resisting system MWFRS of the building. A o 001A g or 4 ft 2 whichever is smaller 262 Table 2613-1 PARTIALLY OPEN BUILDING. I am designing the attachment of cladding on the underside of a roof overhang using ASCE 7-05 for the wind load determination.
When viewing the wind maps take the highest category number of the defined Risk or Occupancy category. Loads in ASCE 7-16 to the design loads determined from ASCE 7-98 through ASCE -05 which collectively formed the basis of the wind criteria in the first three editions of the FBC. A worked example illustrates the method for obtaining design wind pressures for a typical retail store in a strip mall using the wind load provisions of Standard ASCESEI 7-10 Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other Structures.
Design of Buildings for Wind. Ratio of ASCE 7-16 to ASCE 7-05 Wind Loads for Worst-Case. In fact when a building is too complex a wind tunnel procedure can be considered.
Wind design of roof systems is one of the more complicated things that an architect deals with during the design of a building. An outline of the overall process for the. Basic Wind Speed V The ASCE 7-10 provides a wind map where the corresponding basic wind speed of a location can be obtained from Figures 265-1A to 1C.
The simplified procedure is for building with a simple diaphragm roof slope less than 10 degrees mean roof height less than 30 feet 9 meters regular shape rigid building. MWFRS pressures should be used for the truss connection loads across the building span. Tables are included that provide data for commercial buildings.
ASCE 7-10 provides two methods for wind load calculation. In the worst-case scenario the induced-wind pressure top and bottom of the overhang will be in the same direction resulting in magnified net pressure acting on the overhang. For components and cladding CC the analytical envelope procedure for low-rise buildings is used to determine design wind pressure.
Overhangs on the leeward and side edges shall have the basic zones pressure applied. A simplified procedure and an analytical procedure. Upper and lower are simultaneously subjected to wind action.
A Guide for ASCE 7-10 Standard Users and Designers of Special Structures Buch gebunden von Emil Simiu bei hugendubelde. Wind Design Manual Based on 2018 IBC and ASCESEI 7-16 3 This condition is expressed for each wall by the following equation. In most cases including this example.
ASCESEI 7-10 similar at 7-16 The. 4 Compute design wind pressures from ASCE 7-16 through selection of wind directionality factor exposure category and surface roughness any topographical effect and the gust effect factor. If the height of the eave varies along the wall the average height shall be used.
If playback doesnt begin shortly try restarting your device. If the canopy is located low on the building it will receive the downdraft effect of the wind flowing down the face of the building. A building that does not comply with the requirements for an open building partially enclosed building or enclosed building.
ASCE Wind Load Introduction - Steel and Concrete Design. The wind load determined by using the GCp factor from figure 6-11B page 56 overhang is the total load on the overhang including pressure from the upper and lower surfaces ref. EFFECTIVE WIND AREA A.
And with the latest version of ASCE 7 Minimum Design Loads For Buildings and Other Structures ASCE 7 it has become that much more challenging for roof system designers and roofing contractors. The following figure shows the net change in the worst-case Zone 3 design pressure from ASCE 7-05 to ASCE 7-16 2007 FBC to 7th Edition 2020 FBC. Nevertheless the code set a standard in determining wind procedure that we require in our design.
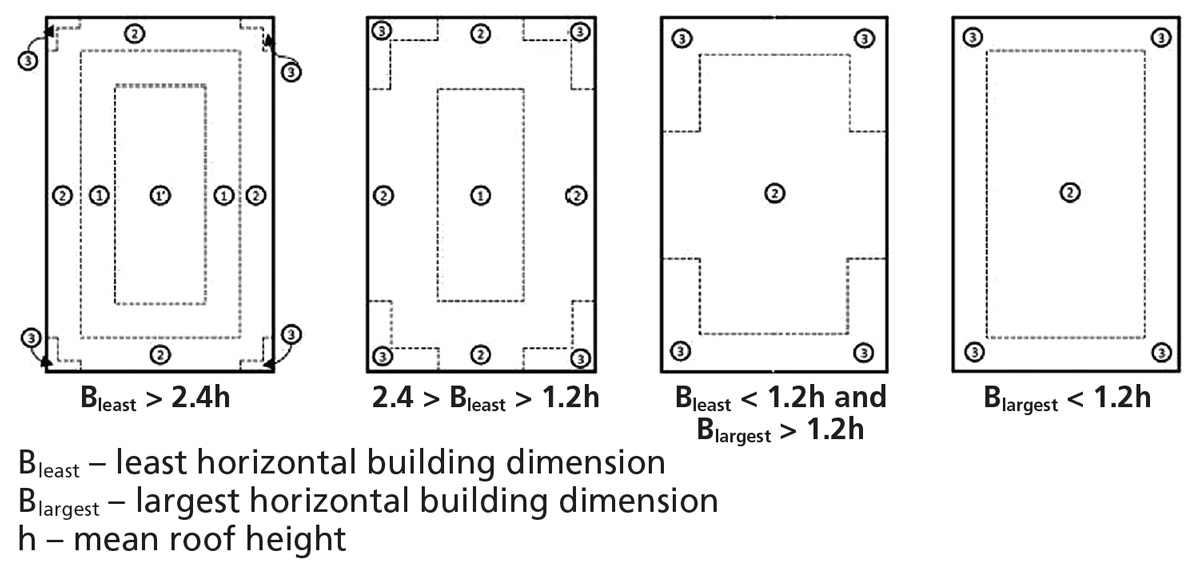
Calculation of Wind Loads on Structures according to ASCE 7-10 Permitted Procedures The design wind loads for buildings and other structures including the Main Wind-Force Resisting System MWFRS and component and cladding elements thereof shall be determined using one of the procedures as specified in the following section. The zones for roof overhangs are different from the zones for a monoslope roof. Different editions of building codes exist and therefore different versions of ASCE.
The Main Wind Force Resisting System MWFRS analytical directional procedure for buildings of any height is used to determine design wind pressure. 3 Determine the basic wind design speed from the mapped values within ASCE 7-16. If the roof is not gable flat or hip the low-rise building provisions of ASCE 7-16 should not be used and the directional procedure for Main Wind Force Resisting Systems MWFRS is used instead.
It is recommended to use a Cp 080 same as the windward wall on the top of the canopy. Equivalent static pressure to be used in the determination of wind loads for buildings EAVE HEIGHT h e. ASCESEI 7-10 same at 7-16 The distance from the ground surface adjacent to the building to the roof eave line at a particular wall.
A Guide for ASCE 7-10 Standard Users and bei eBay. The Occupancy Category is defined and classified in the International Building Code.

Design Of Buildings For Wind A Guide For Asce 7 10 Standard Users And Designers Of Special Structures 2nd Edition Wiley

Examples Mcgraw Hill Education Access Engineering

Wind Loads The Asce 7 Provisions Ce 694

Wind Loads On Buildings Mwfrs Directional Procedure Mcgraw Hill Education Access Engineering

The Typical Floor Plan And Elevation Of A Six Story Office Building Measuring 100 Ft 100 Ft In Plan And Laterally Braced With Ordinary Moment Resisting Frames Is Shown In Figure 3 16 The

Wind Loads On Low Buildings In The Wake Of Alan Davenport S Contributions Sciencedirect

Asce 7 95 Minimum Design Loads For Buildings And Other Structures Paktechpoint

Asce 7 95 Minimum Design Loads For Buildings And Other Structures Paktechpoint

Elevated Building On Posts Wind Load On Bottom Structural Engineering General Discussion Eng Tips
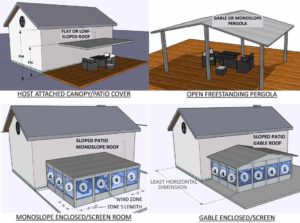
What Is A Canopy Awning Which Wind Forces Should I Use To Design Engineering Express

Pin On Structuraldetails Store Catalogue

Asce 7 95 Minimum Design Loads For Buildings And Other Structures Paktechpoint
Open Front Structure Wind Pressure Design Simpson Strong Tie Structural Engineering Blog

Session 7 Applications Of Asce 7 10 Low Rise Building Ppt Video Online Download

Wind Load Calculations Free Wind Load Calculator

Pdf Wind Loads On Walls Of Low Rise Building

Structure Magazine Asce 7 16 Wind Load Provisions

Wind Loads On Buildings Mwfrs Directional Procedure Mcgraw Hill Education Access Engineering

Asce 7 95 Minimum Design Loads For Buildings And Other Structures Paktechpoint
Comments
Post a Comment